「Raspbian「stretch」上にGO言語をインストール」でGo言語をインストールしましたが、今回は、スイッチ、RGB LED、OLED,圧電ブザーを組み合わせて動作させます。アプリはWindows10上のVisual Studio Codeで開発し、Raspberry Pi上で動作させます。
開発環境
- Raspbian:buster
- go言語のバージョン:go1.13.4
- コーディング環境:Visual Studio Code 1.44.2
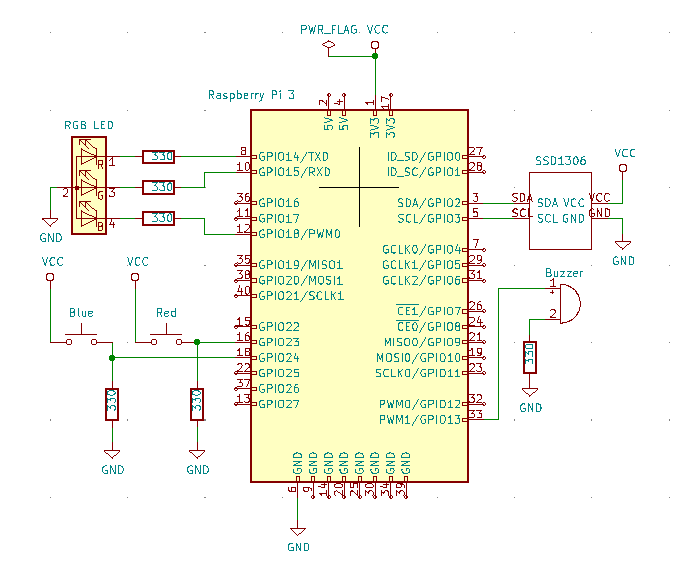
Raspberry Piとスイッチ、RGB LED、OLED,圧電ブザーとの接続
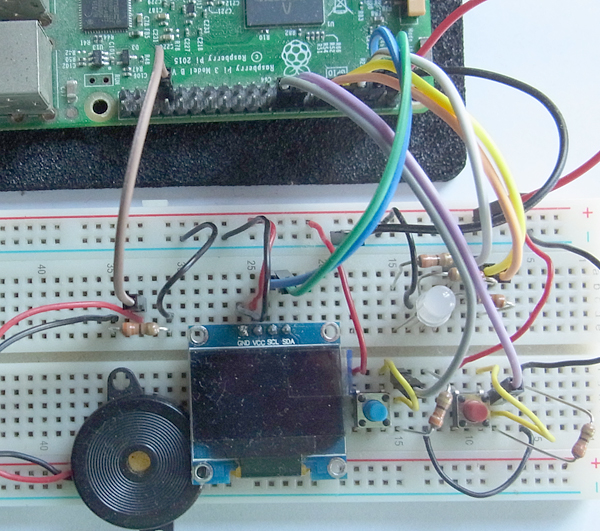
Raspberry Piとスイッチ、RGB LED、OLED,圧電ブザーとを接続した回路図を次に示します。
接続画像を次に示します。
作成するアプリの仕様
作成するアプリの仕様を次に示します。
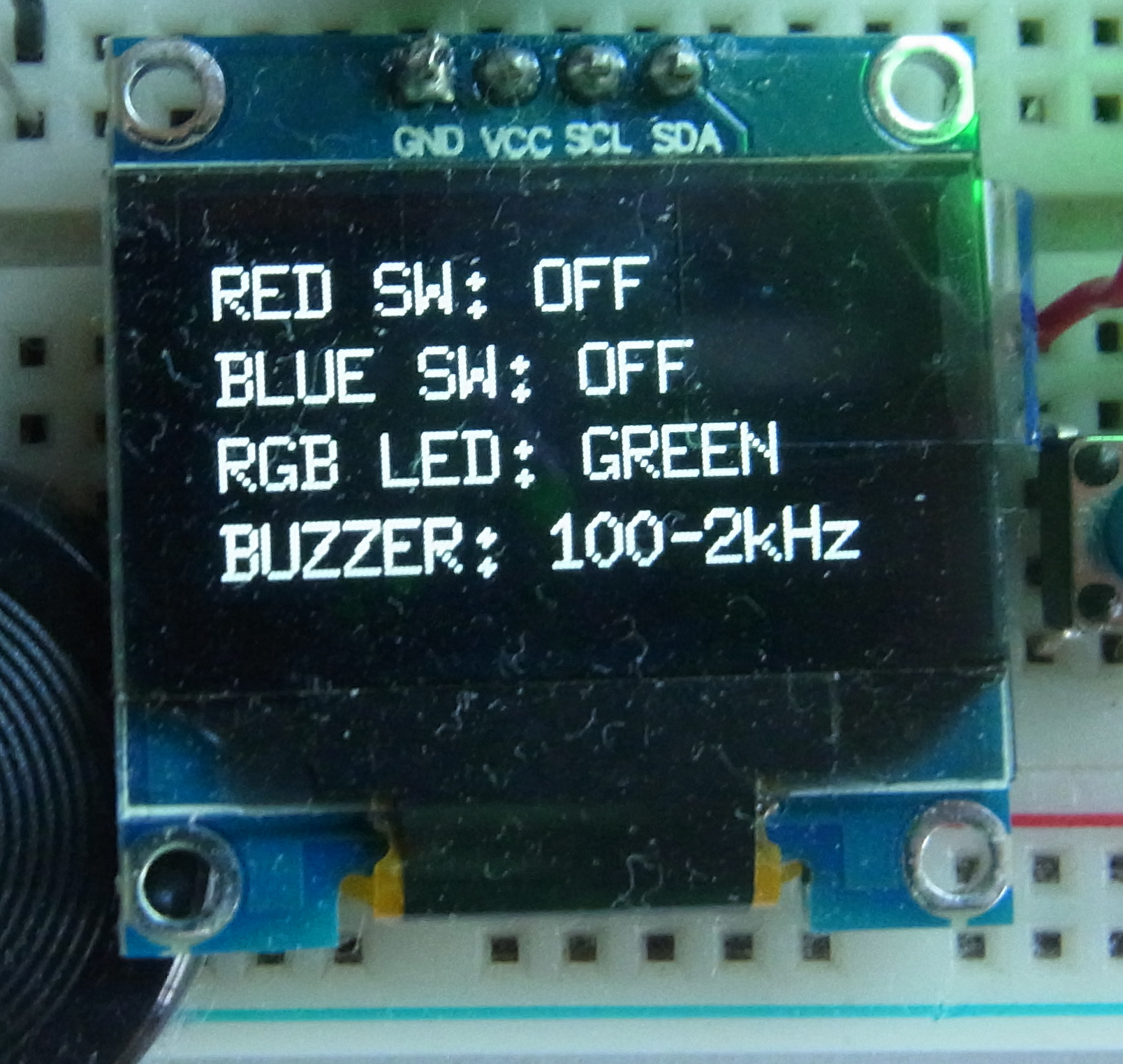
1. アプリを起動すると、
2. スイッチ「赤」を押すと、
- RGB LED:5秒間「赤」の点灯
- 圧電ブザー:5秒間320Hz
- OLED:「RED」の表示
3. スイッチ「青」を押すと、
- RGB LED:5秒間「青」の点灯
- 圧電ブザー:5秒間840Hz
- OLED:「BLUE」の表示
4. スイッチの入力がない場合、アプリの起動画面を再表示します。
アプリの作成
作業フォルダ「gomain」に次に示す「main.go」「text.go」「button.go」「led.go」「buzzer.go」を作成します。
1.使用するチャンネルを次に示します。
| チャンネル名 | 機能 | 発生/使用 |
|---|---|---|
| buzzerch | スイッチが押されたことを通知 | スイッチ「赤」もしくは「青」が押されたとき、「button.go」から「buzzer.go」に通知される。 |
| ledch | スイッチが押されたことを通知 | スイッチ「赤」もしくは「青」が押されたとき、「button.go」から「led.go」に通知される。 |
| textch | SSD1306に表示するデータの転送 | スイッチが押されたとき、LEDを点灯するとき、圧電ブザーを鳴らすときに、「button.go」「led.go」「buzzer.go」から「main.go」に表示データが通知される。 |
| quit | シグナルが発生したことを通知 | キーボードでコントロール-Cが押されたとき、シグナルが発生し、「main.go」に通知される。 |
2.使用するパッケージを次に示します。
- 「periph.io/x/periph/host」
- 「periph.io/x/periph/conn/gpio」
- 「periph.io/x/periph/conn/gpio/gpioreg」
- 「periph.io/x/periph/conn/physic」
- 「periph.io/x/periph/host/rpi」
メインルーチン「main」と初期化ルーチン「init」を次に示します。
- 初期化ルーチンで、シグナルが発生すると通知するようにsignal.Notify関数を呼び、host.Init関数でドライバを初期化します。
- 57行目で表示要求を受け取ります。
- 67行目で終了要求を受け取り、ループ状態から抜け出てブザーの設定を解除します。
main.go
package main
import (
"log"
"os"
"os/signal"
"periph.io/x/periph/host"
)
const (
REDSW int = iota
BLUESW
)
const (
INIT int = iota
REDSTATUS
BLUESTATUS
RGBLED
BUZZER
)
type Display struct {
ID int
data string
}
var buzzerch = make(chan int)
var ledch = make(chan int)
var textch = make(chan Display)
// シグナル用のチャネル定義
var quit = make(chan os.Signal)
func init() {
signal.Notify(quit, os.Interrupt)
// Load all the drivers:
if _, err := host.Init(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
textinit()
textdisplay(Display{INIT, ""})
// 受け取るシグナルを設定
}
func main() {
go button()
go buzzer()
go led()
LOOP:
for {
select {
case display := <-textch:
log.Printf("main %+v\n", display)
textdisplay(display)
case <-quit:
log.Println("signal!")
break LOOP
}
}
if err := pbuzzer.Halt(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
log.Println("Exit")
}
テキストルーチン「textdisplay」とテキスト初期化ルーチン「textinit」を次に示します。詳細については、「Go言語によるSSD1306への表示」を参照してください。
- 表示を更新する場合、再度表示バッファ領域を確保して、すべての情報を設定しなおし、再描画します。
text.go
package main
import (
"image"
"image/color"
"log"
"golang.org/x/image/font"
"golang.org/x/image/font/basicfont"
"golang.org/x/image/math/fixed"
"periph.io/x/periph/conn/i2c/i2creg"
"periph.io/x/periph/devices/ssd1306"
)
const (
REDCNST string = "RED SW: "
BLUECNST string = "BLUE SW: "
RGBCNST string = "RGB LED: "
BUZZERCNST string = "BUZZER: "
)
var dev *ssd1306.Dev
var DefaultOpts = ssd1306.Opts{
W: 128,
H: 64,
Rotated: false,
Sequential: false,
SwapTopBottom: false,
}
var reddata string
var bluedata string
var rgbdata string
var buzzerdata string
func textinit() {
// Open a handle to the first available I?C bus:
bus, err := i2creg.Open("")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
dev, err = ssd1306.NewI2C(bus, &DefaultOpts)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
func textdisplay(display Display) {
img := image.NewGray(image.Rect(0, 0, 128, 64))
dfont := &font.Drawer{
Dst: img,
Src: image.NewUniform(color.Gray{255}),
Face: basicfont.Face7x13,
}
switch display.ID {
case INIT:
reddata = REDCNST + "OFF"
bluedata = BLUECNST + "OFF"
rgbdata = RGBCNST + "SHADE"
buzzerdata = BUZZERCNST + "216-2kHz"
case REDSTATUS:
reddata = REDCNST + display.data
case BLUESTATUS:
bluedata = BLUECNST + display.data
case RGBLED:
rgbdata = RGBCNST + display.data
case BUZZER:
buzzerdata = BUZZERCNST + display.data
default:
log.Println("what !")
}
dfont.Dot = fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(5 * 64), fixed.Int26_6((15 + (0 * 15)) * 64)}
dfont.DrawString(reddata)
dfont.Dot = fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(5 * 64), fixed.Int26_6((15 + (1 * 15)) * 64)}
dfont.DrawString(bluedata)
dfont.Dot = fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(5 * 64), fixed.Int26_6((15 + (2 * 15)) * 64)}
dfont.DrawString(rgbdata)
dfont.Dot = fixed.Point26_6{fixed.Int26_6(5 * 64), fixed.Int26_6((15 + (3 * 15)) * 64)}
dfont.DrawString(buzzerdata)
dev.Draw(img.Bounds(), img, image.Point{})
}
ボタンルーチン「button」を次に示します。「Button」を参考にして作成しました。
- 100msごとに、スイッチ「赤」と「青」の立ち上がりエッジを検出します。
button.go
package main
import (
"log"
"time"
"periph.io/x/periph/conn/gpio"
"periph.io/x/periph/conn/gpio/gpioreg"
)
func button() {
// Lookup a pin by its number:
redbutton := gpioreg.ByName("GPIO23")
if redbutton == nil {
log.Fatal("Failed to find GPIO23")
}
log.Printf("%s: %s\n", redbutton, redbutton.Function())
// Lookup a pin by its number:
bluebutton := gpioreg.ByName("GPIO24")
if bluebutton == nil {
log.Fatal("Failed to find GPIO24")
}
log.Printf("%s: %s\n", bluebutton, bluebutton.Function())
// Set it as input, with an internal pull down resistor:
if err := redbutton.In(gpio.PullDown, gpio.RisingEdge); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Set it as input, with an internal pull down resistor:
if err := bluebutton.In(gpio.PullDown, gpio.RisingEdge); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Wait for edges as detected by the hardware, and print the value read:
for {
if redbutton.WaitForEdge(0) {
//if redbutton.edge != gpio.NoEdge {
log.Printf("redbutton -> %s\n", redbutton.Read())
buzzerch <- REDSW
ledch <- REDSW
textch <- Display{REDSTATUS, "ON"}
textch <- Display{BLUESTATUS, "OFF"}
}
if bluebutton.WaitForEdge(0) {
//if redbutton.edge != gpio.NoEdge {
log.Printf("bluebutton -> %s\n", bluebutton.Read())
buzzerch <- BLUESW
ledch <- BLUESW
textch <- Display{REDSTATUS, "OFF"}
textch <- Display{BLUESTATUS, "ON"}
}
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
}
}
LEDルーチン「led」を次に示します。「LED」を参考にして作成しました。
- 14行目でチャンネル「ledch」を監視し、表示要求のない場合はLED「緑」を表示します。
led.go
package main
import (
"log"
"time"
"periph.io/x/periph/conn/gpio"
"periph.io/x/periph/host/rpi"
)
func led() {
for {
select {
case command := <-ledch:
log.Printf("led %d\n", command)
switch command {
case REDSW:
textch <- Display{RGBLED, "RED"}
if err := rpi.P1_8.Out(gpio.High); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err := rpi.P1_10.Out(gpio.Low); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err := rpi.P1_12.Out(gpio.Low); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
case BLUESW:
textch <- Display{RGBLED, "BLUE"}
if err := rpi.P1_8.Out(gpio.Low); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err := rpi.P1_10.Out(gpio.Low); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err := rpi.P1_12.Out(gpio.High); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
default:
textch <- Display{RGBLED, "GREEN"}
if err := rpi.P1_8.Out(gpio.Low); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err := rpi.P1_10.Out(gpio.High); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err := rpi.P1_12.Out(gpio.Low); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
}
}
圧電ブザールーチン「buzzer」を次に示します。「Buzzer」を参考にして作成しました。
- 要求がない場合は、14行目のsound関数を呼び出し、5秒間で100Hzから2kHzまで周波数を更新します。
buzzer.go
package main
import (
"log"
"time"
"periph.io/x/periph/conn/gpio"
"periph.io/x/periph/conn/gpio/gpioreg"
"periph.io/x/periph/conn/physic"
)
var pbuzzer gpio.PinIO
func sound() {
for i := 0; i < 19; i++ {
if err := pbuzzer.PWM(gpio.DutyHalf, 100*physic.Frequency(i+1)*physic.Hertz); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
time.Sleep(250 * time.Millisecond)
}
}
func buzzer() {
pbuzzer = gpioreg.ByName("PWM1_OUT")
if pbuzzer == nil {
log.Fatal("Failed to find buzzer")
}
for {
select {
case command := <-buzzerch:
log.Printf("buzzer %d\n", command)
switch command {
case REDSW:
textch <- Display{BUZZER, "320Hz"}
if err := pbuzzer.PWM(gpio.DutyHalf, 320*physic.Hertz); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
case BLUESW:
textch <- Display{BUZZER, "840Hz"}
if err := pbuzzer.PWM(gpio.DutyHalf, 840*physic.Hertz); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
}
default:
textch <- Display{BUZZER, "100-2kHz"}
sound()
}
if err := pbuzzer.Halt(); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
}
アプリの実行
次のコマンドでコンパイルして実行します。
$ go build
$ sudo ./gomain
2020/05/17 15:41:50 GPIO23: In/Low
2020/05/17 15:41:50 GPIO24: In/Low
2020/05/17 15:41:50 main {ID:3 data:GREEN}
2020/05/17 15:41:50 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
2020/05/17 15:41:54 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
2020/05/17 15:41:55 main {ID:3 data:GREEN}
2020/05/17 15:41:59 redbutton -> High
2020/05/17 15:41:59 buzzer 0
2020/05/17 15:41:59 main {ID:4 data:320Hz}
2020/05/17 15:42:00 led 0
2020/05/17 15:42:00 main {ID:3 data:RED}
2020/05/17 15:42:00 main {ID:1 data:ON}
2020/05/17 15:42:00 main {ID:2 data:OFF}
2020/05/17 15:42:04 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
2020/05/17 15:42:05 main {ID:3 data:GREEN}
2020/05/17 15:42:09 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
2020/05/17 15:42:10 main {ID:3 data:GREEN}
2020/05/17 15:42:10 bluebutton -> High
2020/05/17 15:42:14 buzzer 1
2020/05/17 15:42:14 main {ID:4 data:840Hz}
2020/05/17 15:42:15 led 1
2020/05/17 15:42:15 main {ID:3 data:BLUE}
2020/05/17 15:42:15 main {ID:1 data:OFF}
2020/05/17 15:42:15 main {ID:2 data:ON}
2020/05/17 15:42:19 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
2020/05/17 15:42:20 main {ID:3 data:GREEN}
2020/05/17 15:42:22 redbutton -> High
2020/05/17 15:42:24 buzzer 0
2020/05/17 15:42:24 main {ID:4 data:320Hz}
2020/05/17 15:42:25 led 0
2020/05/17 15:42:25 main {ID:1 data:ON}
2020/05/17 15:42:25 main {ID:2 data:OFF}
2020/05/17 15:42:25 main {ID:3 data:RED}
2020/05/17 15:42:29 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
2020/05/17 15:42:30 main {ID:3 data:GREEN}
2020/05/17 15:42:33 bluebutton -> High
2020/05/17 15:42:33 buzzer 1
2020/05/17 15:42:33 main {ID:4 data:840Hz}
2020/05/17 15:42:35 led 1
2020/05/17 15:42:35 main {ID:1 data:OFF}
2020/05/17 15:42:35 main {ID:2 data:ON}
2020/05/17 15:42:35 main {ID:3 data:BLUE}
2020/05/17 15:42:38 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
2020/05/17 15:42:40 main {ID:3 data:GREEN}
2020/05/17 15:42:43 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
2020/05/17 15:42:45 main {ID:3 data:GREEN}
2020/05/17 15:42:48 main {ID:4 data:100-2kHz}
^C2020/05/17 15:42:49 signal!
2020/05/17 15:42:49 Exit
アプリ実行中の動画を次に示します。